Kubernetes Free TLS Certificate Management
How to Create and Manage TLS Certificates for Free on a Kubernetes cluster with Nginx and cert-manager.
Using HTTPS to publish your website or expose your API is a must nowadays. Luckily, long gone are the days where you needed to spend hundreds of dollars and time to create and manage a valid TLS / SSL certificate. In this tutorial, I will explain how to fully automate the process of requesting and configuring your certificates in a Kubernetes cluster using cert-manager, Let’s Encrypt and the Nginx Ingress Controller.
While the installation and configuration of cert-manager is extremely trivial, I would classify this tutorial as advanced because of its prerequisites. I actually started writing this post in November 2019 but never published because it was too long and complicated, so I decided to skip the prerequisites setup. If you are looking for this solution, my expectation is that you already have a working Kubernetes cluster with some of your applications exposed to the public internet. If you don’t, I would advice you to read the following tutorials first:
- Easiest Kubernetes Install ever! Certified Kubernetes with just one command line
- Install Nginx Ingress Controller on Kubernetes and MicroK8s
Create the DNS record
Before we proceed with the installation of cert-manager, it is best to create the DNS record so we give it chance to propagate over the internet. You need to point the record to the public IP of your exposed Kubernetes Ingress Controller. Feel free to comment below if you have a hard time understanding how to do this.
Pro Tip: Avoid hitting your domain name before creating the record to avoid negative caching.
Installing cert-manager
To install cert-manager, just execute the following:
kubectl create namespace cert-manager
kubectl apply --validate=false -f https://github.com/jetstack/cert-manager/releases/download/v1.0.3/cert-manager.yamlWe verify if the relevant Pods are running.
marcol@ubuntu:~$ kubectl get pods -n cert-manager
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
cert-manager-5c47f46f57-jpv29 1/1 Running 0 4m
cert-manager-cainjector-6659d6844d-wn4nj 1/1 Running 1 4m
cert-manager-webhook-547567b88f-xtnwx 1/1 Running 0 4mIntegrating Let’s Encrypt
A compelling thing about cert-manager is its support for multiple types of certificate issuers: SelfSigned, CA, Vault, Venafi, External and ACME. Multiple issuers can be configured per cluster and each Ingress defines which issuer it wants to use for the management of its certificates.
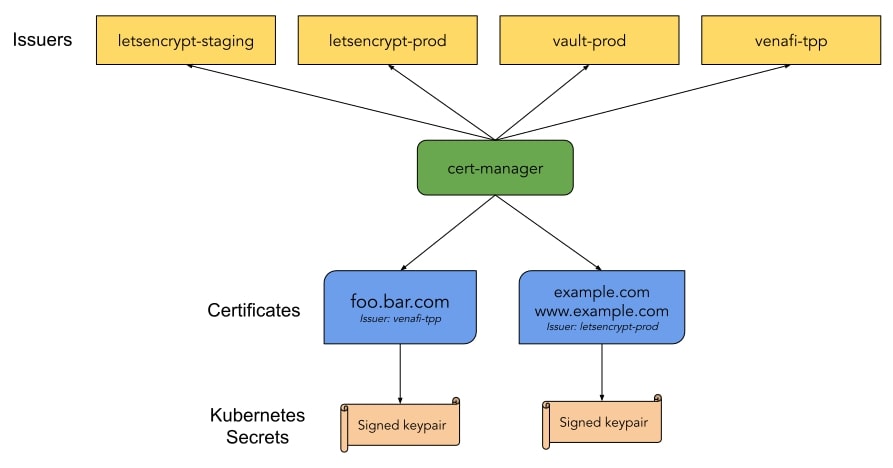
Let’s Encrypt is a nonprofit Certificate Authority that provides free TLS certificates to over 200 million websites already. It provides certificates through an automated system that falls under the Automated Certificate Management Environments (ACME) category.
Pro Tip: Let’s Encrypt has strict rate limits! Always test your configurations against the staging Issuer. Use the production Issuer only when you are 100% confident everything is configured correctly.
Create a Deployment
You will most probably have already a deployment in mind for which you want to automate TLS management. If you do not, let’s just use the sample deployment and service offered by cert-manager named kuard.
kubectl apply -f https://netlify.cert-manager.io/docs/tutorials/acme/example/deployment.yaml
kubectl apply -f https://netlify.cert-manager.io/docs/tutorials/acme/example/service.yamlConfigure Let’s Encrypt Issuer
Let’s setup two Issuer resources: one for staging and the other for production. An Issuer is a special Kubernetes resource that represents a CA able to generate signed certificates by honoring certificate signing requests. Type the following command to be able to edit the definition before applying it to your cluster.
kubectl create --edit -f https://cert-manager.io/docs/tutorials/acme/example/staging-issuer.yamlEdit the YAML by replacing the email address with the one you want to use during certificate registration.
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: Issuer
metadata:
name: letsencrypt-staging
spec:
acme:
# The ACME server URL
server: https://acme-staging-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory
# Email address used for ACME registration
email: [email protected]
# Name of a secret used to store the ACME account private key
privateKeySecretRef:
name: letsencrypt-staging
# Enable the HTTP-01 challenge provider
solvers:
- http01:
ingress:
class: nginxLet’s repeat the same procedure for the production Issuer as well.
kubectl create --edit -f https://cert-manager.io/docs/tutorials/acme/example/production-issuer.yaml apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: Issuer
metadata:
name: letsencrypt-prod
spec:
acme:
# The ACME server URL
server: https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory
# Email address used for ACME registration
email: [email protected]
# Name of a secret used to store the ACME account private key
privateKeySecretRef:
name: letsencrypt-prod
# Enable the HTTP-01 challenge provider
solvers:
- http01:
ingress:
class: nginxLet’s check the status of our issuers.
kubectl describe issuer letsencrypt-staging
Name: letsencrypt-staging
Namespace: default
Labels: <none>
Annotations: kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration={"apiVersion":"cert-manager.io/v1","kind":"Issuer","metadata":{"annotations":{},"name":"letsencrypt-staging","namespace":"default"},(...)}
API Version: cert-manager.io/v1
Kind: Issuer
Metadata:
Cluster Name:
Creation Timestamp: 2018-11-17T18:03:54Z
Generation: 0
Resource Version: 9092
Self Link: /apis/cert-manager.io/v1/namespaces/default/issuers/letsencrypt-staging
UID: 25b7ae77-ea93-11e8-82f8-42010a8a00b5
Spec:
Acme:
Email: [email protected]
Private Key Secret Ref:
Key:
Name: letsencrypt-staging
Server: https://acme-staging-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory
Solvers:
Http 01:
Ingress:
Class: nginx
Status:
Acme:
Uri: https://acme-staging-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/acme/acct/7374163
Conditions:
Last Transition Time: 2018-11-17T18:04:00Z
Message: The ACME account was registered with the ACME server
Reason: ACMEAccountRegistered
Status: True
Type: Ready
Events: <none>Define a Kubernetes Ingress with automatic TLS enabled
This is this last step where the fun starts. We will be defining a Kubernetes Ingress pointing to our domain while instructing cert-manager to handle all the TLS voodoo to register our certificate and expose it automatically for our application. This is not all, cert-manager will also take care of renewing the certificate before it’s expiration date. Oh yeah!
kubectl create --edit -f https://cert-manager.io/docs/tutorials/acme/example/ingress-tls.yamlapiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: kuard
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: "nginx"
# Remember our pro-tip. We test stuff against the staging issuer. Always!!!
cert-manager.io/issuer: "letsencrypt-staging"
spec:
tls:
- hosts:
# Set this to your target domain
- example.example.com
# You can use any name you prefer. Do not have multiple ingresses use the same one though.
secretName: quickstart-example-tls
rules:
- host: example.example.com
http:
paths:
- path: /
backend:
serviceName: kuard
servicePort: 80That’s all! Wait for the magic to happen! We can track the certificate registration process by inspecting the certificate resource.
kubectl describe certificate quickstart-example-tls
Name: quickstart-example-tls
Namespace: default
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
API Version: cert-manager.io/v1
Kind: Certificate
Metadata:
Cluster Name:
Creation Timestamp: 2018-11-17T17:58:37Z
Generation: 0
Owner References:
API Version: extensions/v1beta1
Block Owner Deletion: true
Controller: true
Kind: Ingress
Name: kuard
UID: a3e9f935-ea87-11e8-82f8-42010a8a00b5
Resource Version: 9295
Self Link: /apis/cert-manager.io/v1/namespaces/default/certificates/quickstart-example-tls
UID: 68d43400-ea92-11e8-82f8-42010a8a00b5
Spec:
Dns Names:
www.example.com
Issuer Ref:
Kind: Issuer
Name: letsencrypt-staging
Secret Name: quickstart-example-tls
Status:
Acme:
Order:
URL: https://acme-staging-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/acme/order/7374163/13665676
Conditions:
Last Transition Time: 2018-11-17T18:05:57Z
Message: Certificate issued successfully
Reason: CertIssued
Status: True
Type: Ready
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal CreateOrder 9m cert-manager Created new ACME order, attempting validation...
Normal DomainVerified 8m cert-manager Domain "www.example.com" verified with "http-01" validation
Normal IssueCert 8m cert-manager Issuing certificate...
Normal CertObtained 7m cert-manager Obtained certificate from ACME server
Normal CertIssued 7m cert-manager Certificate issued SuccessfullyIf the certificate was issued successfully, we’re good to switch to our production issuer.
kubectl create --edit -f https://cert-manager.io/docs/tutorials/acme/example/ingress-tls-final.yamlapiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: kuard
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: "nginx"
# We are switching to prod! Yay!
cert-manager.io/issuer: "letsencrypt-prod"
spec:
tls:
- hosts:
# Do not forget to define your domain
- example.example.com
secretName: quickstart-example-tls
rules:
- host: example.example.com
http:
paths:
- path: /
backend:
serviceName: kuard
servicePort: 80Since we had already quickstart-example-tls secret created we must delete it so that cert-manager replaces it with a new one.
kubectl delete secret quickstart-example-tlsDone! Just access your website and be proud of yourself 🙂
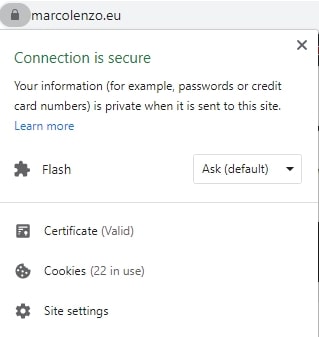
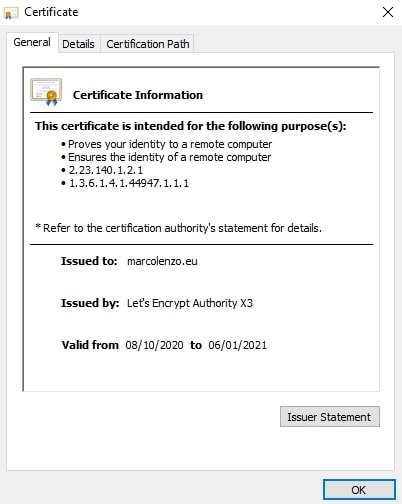
Conclusion
Long gone are the times where obtaining a TLS certificate is pricey and cumbersome. Setup cert-manager in your Kubernetes cluster once and enjoy free automated TLS certificate registration and management. Use your spare time for your hobbies!
Feel free to comment if you need help with something!